Blog
ILLINOIS' PREMIER
MOVING EXPERTS










Best Local Movers
Are you moving soon?
You’re going to need local movers. We think those movers should be us! We offer the best rates, and our movers are friendly, fast, and efficient. They will do everything they can to make your move as easy as possible. We have been in business for years so we know what it takes to get the job done right!
Our team of professional movers is always ready when you are – no matter how big or small your load may be. So go ahead and give us a call today. Let us take care of all your moving needs from start to finish with our full-service approach. We look forward to hearing from you soon!
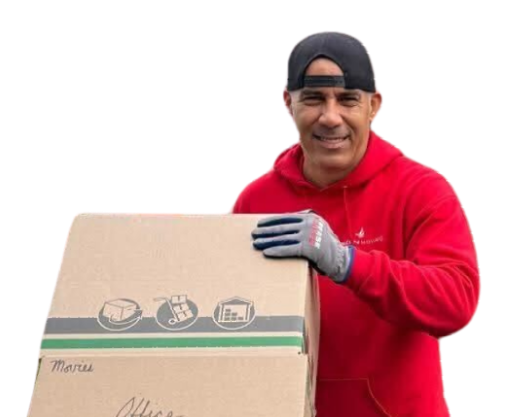


Where Efficiency Takes Flight—Choose Falcon

Where Efficiency Takes Flight—Choose Falcon
Why Choose Us?
Reliable
Our team is dedicated to providing reliable service with an unparalleled level of care for our customers' belongings.
On-Time
We take the stress out of moving with punctual, reliable service designed for your ease.
Licensed
We are fully licensed, and background checked so you know your valuables are in good hands when they're with us!
Insured
We're insured and proud to hold an A+ BBB rating. With Falcon Moving, every detail is handled by professionals who take pride in their work.
See Us In Action
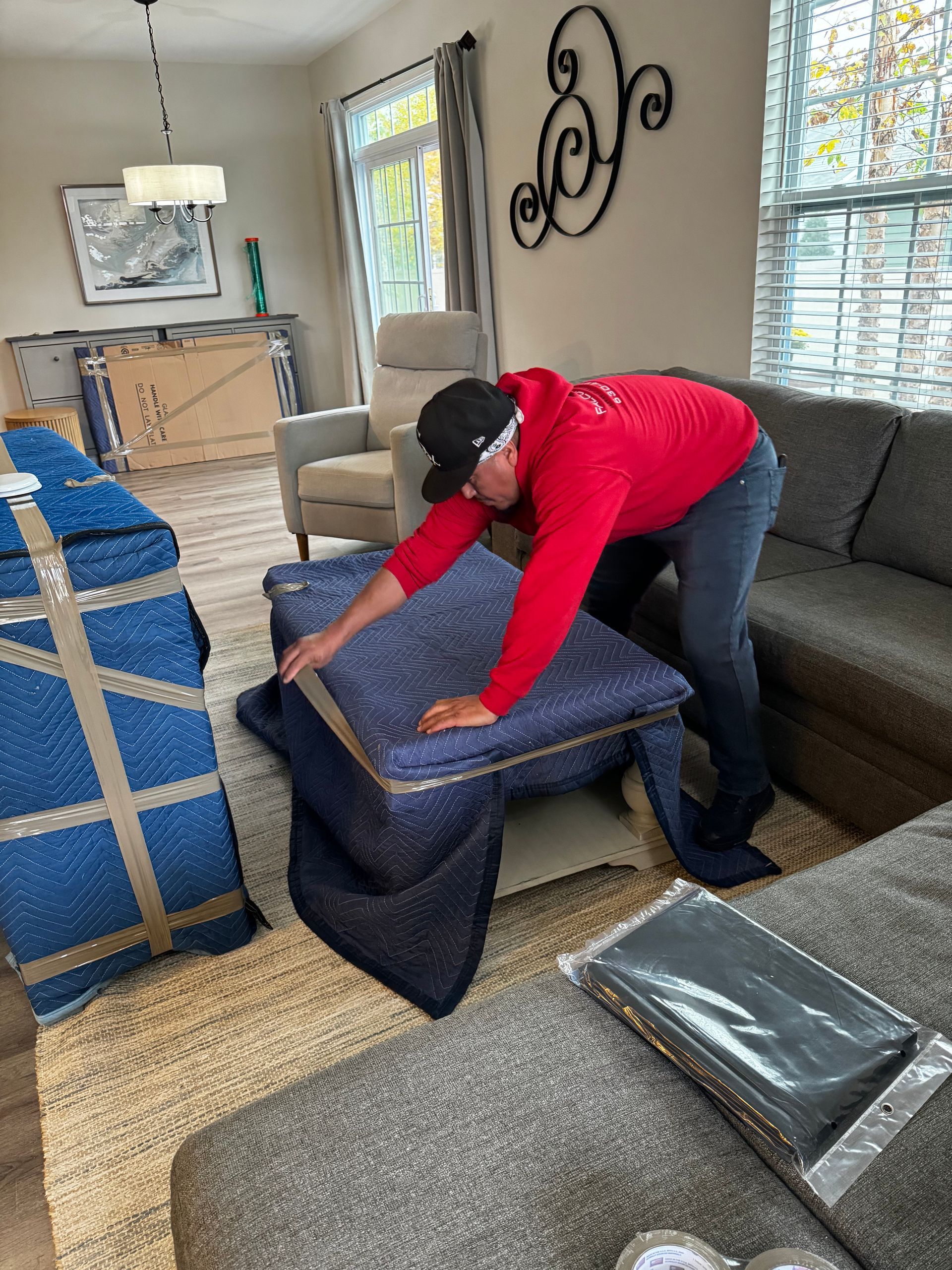

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton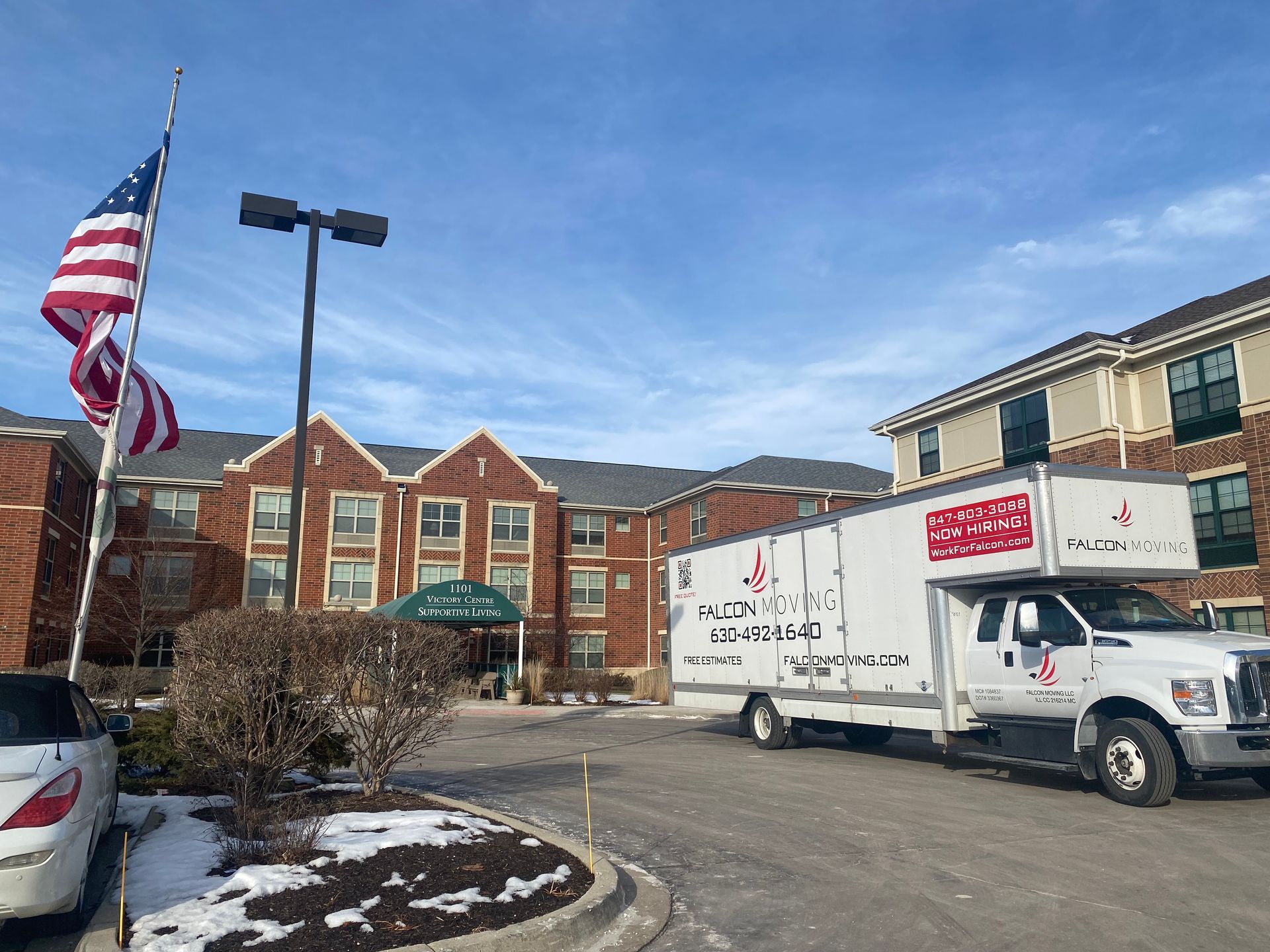
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton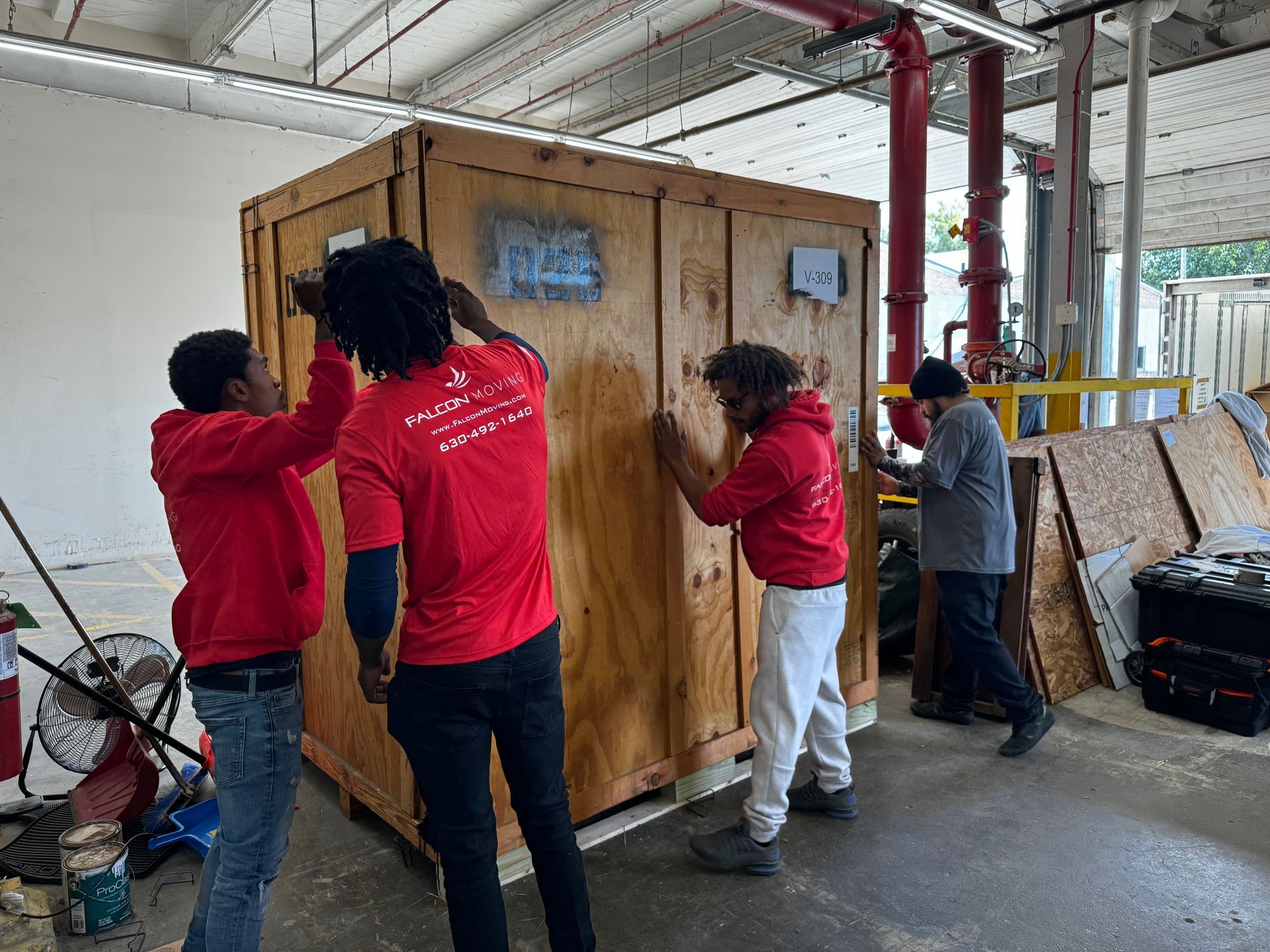
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton


